常用开发设计模式:单例模式、工厂模式、观察者模式、装饰者模式,列举
单例模式
保证一个类只有一个实例,提供一个全局访问的点
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class SingletonClass{
private static SingletonClass singletonClass;
public static SingletonClass newInstance(){
if(singletonClass==null){
synchronized(SingletonClass.class){
if(singletonClass==null){
singletonClass = new SingletonClass();
}
}
}
return singletonClass;
}
}
|
工厂模式
不会对客户端暴露创建对象的逻辑,并且通过同一个接口来指定新创建的对象
图解:

1、创建一个公共接口
1
2
3
| public interface Shape{
void draw();
}
|
2、 定义具体的对象
画圆形:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| public Circle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Square::draw() method.");
}
}
|
画矩形:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| public class Rectangle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Inside Rectangle::draw() method.");
}
}
|
3、创建工厂,生成基于给定信息的实体类的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| public class ShapeFactory {
public Shape getShape(String shapeType){
if(shapeType == null){
return null;
}
if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")){
return new Circle();
} else if(shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("RECTANGLE")){
return new Rectangle();
}
return null;
}
}
|
4、调用具体的对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class FactoryPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShapeFactory shapeFactory = new ShapeFactory();
Shape shape1 = shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE");
shape1.draw();
Shape shape2 = shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE");
shape2.draw();
}
}
|
观察者模式(发布订阅模式)
观察者模式又名发布订阅模式,通俗点可以理解为如下图:
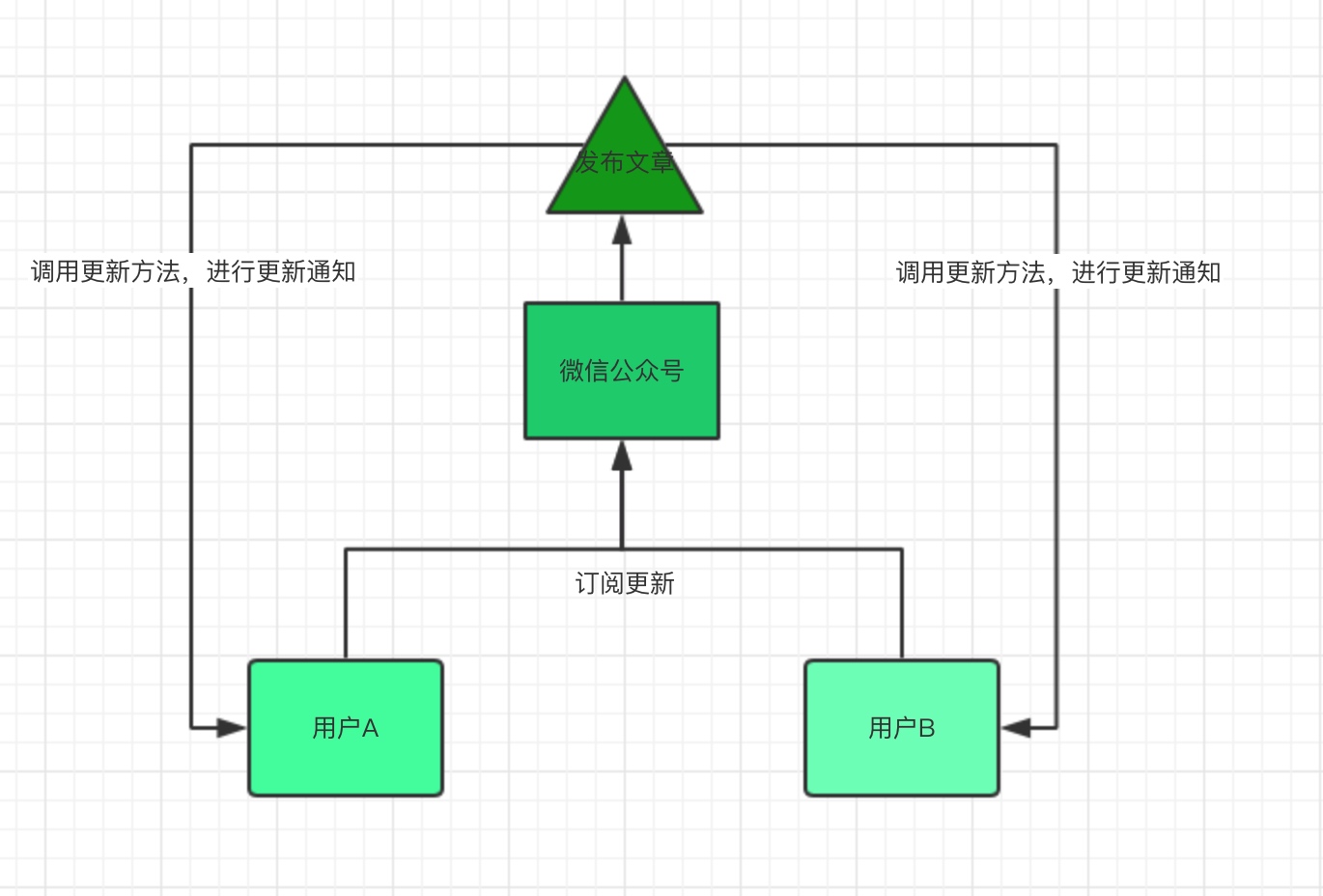
实例代码:
抽象观察者(用户)
//定义一个更新方法,即发布文章之后的通知
1
2
3
| public interface Observer {
public void update(String message);
}
|
具体观察者(关注公众号用户)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class WeixinUser implements Observer {
private String name;
public WeixinUser(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void update(String message) {
System.out.println(name + "-" + message);
}
}
|
被观察者(公众号)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public interface Subject {
public void attach(Observer observer);
public void detach(Observer observer);
public void notify(String message);
}
|
具体的别观察者(公众号具体方法)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| public class SubscriptionSubject implements Subject {
private List<Observer> weixinUserlist = new ArrayList<Observer>();
@Override
public void attach(Observer observer) {
weixinUserlist.add(observer);
}
@Override
public void detach(Observer observer) {
weixinUserlist.remove(observer);
}
@Override
public void notify(String message) {
for (Observer observer : weixinUserlist) {
observer.update(message);
}
}
}
|
测试:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SubscriptionSubject mSubscriptionSubject=new SubscriptionSubject();
WeixinUser user1=new WeixinUser("用户1");
WeixinUser user1=new WeixinUser("用户2");
WeixinUser user1=new WeixinUser("用户3");
mSubscriptionSubject.attach(user1);
mSubscriptionSubject.attach(user2);
mSubscriptionSubject.attach(user3);
mSubscriptionSubject.notify("文章更新了");
}
}
|
装饰者模式
动态的给对象添加一些额外的属性或行为。
举例子:
存在一个蛋糕,我们需要计算蛋糕装饰上蜡烛和水果之后的价格
1、定义组件类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| public abstract class Sweet {
String description = "Sweet";
public String getDescription() {
return description;
}
public abstract double cost();
}
|
2、定义被装饰者「蛋糕」类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class Cake extends Sweet {
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return "一个蛋糕";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return 66;
}
}
|
3、定义装饰器
1
2
3
| public abstract class Decorator extends Sweet {
public abstract String getDescription();
}
|
4、定义装饰者水果和蜡烛类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
public class FruitDecorator extends Decorator {
Sweet sweet;
public FruitDecorator(Sweet sweet) {
this.sweet = sweet;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return sweet.getDescription() + ",水果";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return sweet.cost() + 10;
}
}
public class CandleDecorator extends Decorator {
Sweet sweet;
public CandleDecorator(Sweet sweet) {
this.sweet = sweet;
}
@Override
public String getDescription() {
return sweet.getDescription() + ",蜡烛";
}
@Override
public double cost() {
return sweet.cost() + 10;
}
}
|
5、调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public static void main(String[] args) {
Cake cake = new Cake();
System.out.println(cake.getDescription() + "总共花费" + cake.cost());
FruitDecorator fruitDecorator = new FruitDecorator(cake);
System.out.println(fruitDecorator.getDescription() + "总共花费" + fruitDecorator.cost());
CandleDecorator candleDecorator = new CandleDecorator(fruitDecorator);
System.out.println(candleDecorator.getDescription() + "总共花费" + candleDecorator.cost());
}
|
输出:
1
2
3
| 一个蛋糕,总共花费66.0
一个蛋糕,水果,总共花费76.0
一个蛋糕,水果,一根蜡烛,总共花费86.0
|

